Introduction
Physiotherapy in Bathurst for Foot
Welcome to Physio Max's patient resource about Accessory Navicular Problems.
Not everyone has the same number of bones in his feet. It is not uncommon for both the hands and the feet to contain extra small accessory bones, or ossicles, that sometimes cause problems.
This article will help you understand:
- where the accessory navicular is located
- why the extra bone can cause problems
- how doctors treat the condition
#testimonialslist|kind:all|display:slider|orderby:type|filter_utags_names:Foot therapy|limit:15|heading:Hear from some of our *Foot Therapy* patients#
Anatomy
Where is the accessory navicular located?
The navicular bone of the foot is one of the small bones on the mid-foot.
Navicular Bone
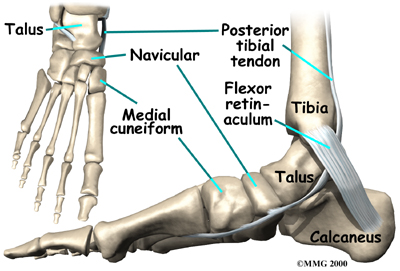
The bone is located at the instep, the arch at the middle of the foot. One of the larger tendons of the foot, called the posterior tibial tendon, attaches to the navicular before continuing under the foot and into the forefoot. This tendon is a tough band of tissue that helps hold up the arch of the foot. If there is an accessory navicular, it is located in the instep where the posterior tibial tendon attaches to the real navicular bone.
Posterior Tibial Tendon
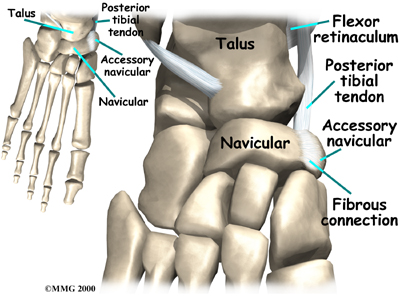
The accessory navicular is a congenital anomaly, meaning that you are born with the extra bone. As the skeleton completely matures, the navicular and the accessory navicular never completely grow, or fuse, into one solid bone. The two bones are joined by fibrous tissue or cartilage. Girls seem to be more likely to have an accessory navicular than boys.
Related Document: Physio Max's Guide to Foot Anatomy
Causes
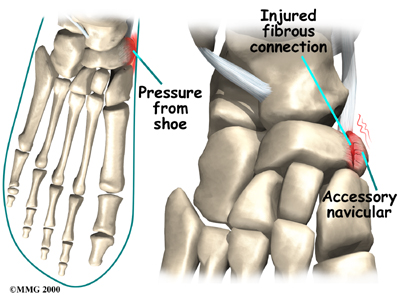 How does an accessory navicular cause problems?
How does an accessory navicular cause problems?
Just having an accessory navicular bone is not necessarily a bad thing. Not all people with these accessory bones have symptoms. Symptoms arise when the accessory navicular is overly large or when an injury disrupts the fibrous tissue between the navicular and the accessory navicular. A very large accessory navicular can cause a bump on the instep that rubs on your shoe causing pain.
An injury to the fibrous tissue connecting the two bones can cause something similar to a fracture. The injury allows movement to occur between the navicular and the accessory bone and is thought to be the cause of pain. The fibrous tissue is prone to poor healing and may continue to cause pain. Because the posterior tibial tendon attaches to the accessory navicular, it constantly pulls on the bone, creating even more motion between the fragments with each step.
Symptoms
What does the condition feel like?
The primary reason an accessory navicular becomes a problem is pain. There is no need to do anything with an accessory navicular that is not causing pain. The pain is usually at the instep area and can be pinpointed over the small bump in the instep. Walking can be painful when the problem is aggravated. As stated earlier, the condition is more common in girls. The problem commonly becomes symptomatic in the teenage years.
Diagnosis
How do health care providers identify the problem?
When you first visit Physio Max, diagnosis of your problem begins with a complete history and physical examination. Usually the condition is suggested by the history and the tenderness over the area of the navicular.
Some patients may be referred to a doctor for further diagnosis. X-rays will usually be required to allow the physician to see the accessory navicular. Generally no other tests are required.
Once your diagnostic examination is complete, the physiotherapists at Physio Max have treatment options that will help speed your recovery, so that you can more quickly return to your active lifestyle.
Our Treatment
What can be done for a painful accessory navicular?
The treatment for a symptomatic accessory navicular can be divided into nonsurgical treatment and surgical treatment. In the vast majority of cases, treatment usually begins with nonsurgical measures. Surgery usually is only considered when all nonsurgical measures have failed to control your problem and the pain becomes intolerable.
Non-surgical Rehabilitation
If the foot becomes painful following a twisting type of injury and an examination reveals the presence of an accessory navicular bone, we may recommend a period of immobilization in a cast or splint. This will rest the foot and perhaps allow the disruption between the navicular and accessory navicular to heal.
Our physiotherapist may recommend the use of an arch support to relieve the stress on the fragment and decrease the symptoms. If the pain subsides and the fragment becomes asymptomatic, further treatment may not be necessary.
Patients with a painful accessory navicular may benefit from more involved physiotherapy treatments. Your physiotherapist may design a series of stretching exercises to try and ease tension on the posterior tibial tendon. We may also recommend the a shoe insert, or orthotic, be used to support the arch and protect the sore area. This approach may allow you to resume normal walking immediately, but you should probably cut back on more vigorous activities for several weeks to allow the inflammation and pain to subside.
Our physiotherapist will apply direct treatments to the painful area to help control pain and swelling. Examples include ultrasound, moist heat, and soft-tissue massage. Our physiotherapy sessions sometimes also include iontophoresis, which uses a mild electrical current to push anti-inflammatory medicine, prescribed by your doctor, into the sore area.
At Physio Max, our goal is to help speed your recovery so that you can more quickly return to your everyday activities. When your recovery is well under way, regular visits to our office will end. We will continue to be a resource, but you will be in charge of doing your exercises as part of an ongoing home program.
Post-surgical Rehabilitation
You may need to use crutches for several days after surgery. A physiotherapist can help you learn to properly use your crutches to avoid putting weight on your foot too soon. Your stitches will be removed about in 10 to 14 days (unless they are the absorbable type, which will not need to be taken out). You should be safe to be released to full activity in about six weeks.
Physio Max provides services for physiotherapy in Bathurst.
Surgery
If all nonsurgical measures fail and the fragment continues to be painful, surgery may be recommended.
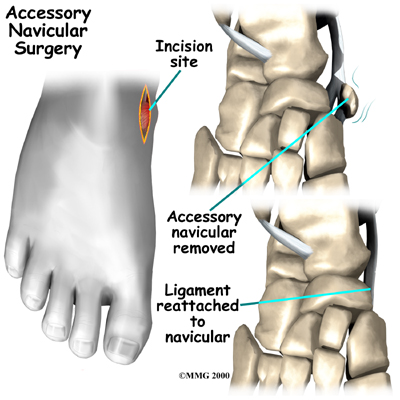
The most common procedure used to treat the symptomatic accessory navicular is the Kidner procedure. A small incision is made in the instep of the foot over the accessory navicular. The accessory navicular is then detached from the posterior tibial tendon and removed from the foot. The posterior tibial tendon is reattached to the remaining normal navicular. Following the procedure, the skin incision is closed with stitches, and a bulky bandage and splint are applied to the foot and ankle.
Portions of this document copyright MMG, LLC.






